New article on ssRNA
Identification and characterization of a novel plaque-invisible lytic single-stranded RNA phage
ABSTRACT
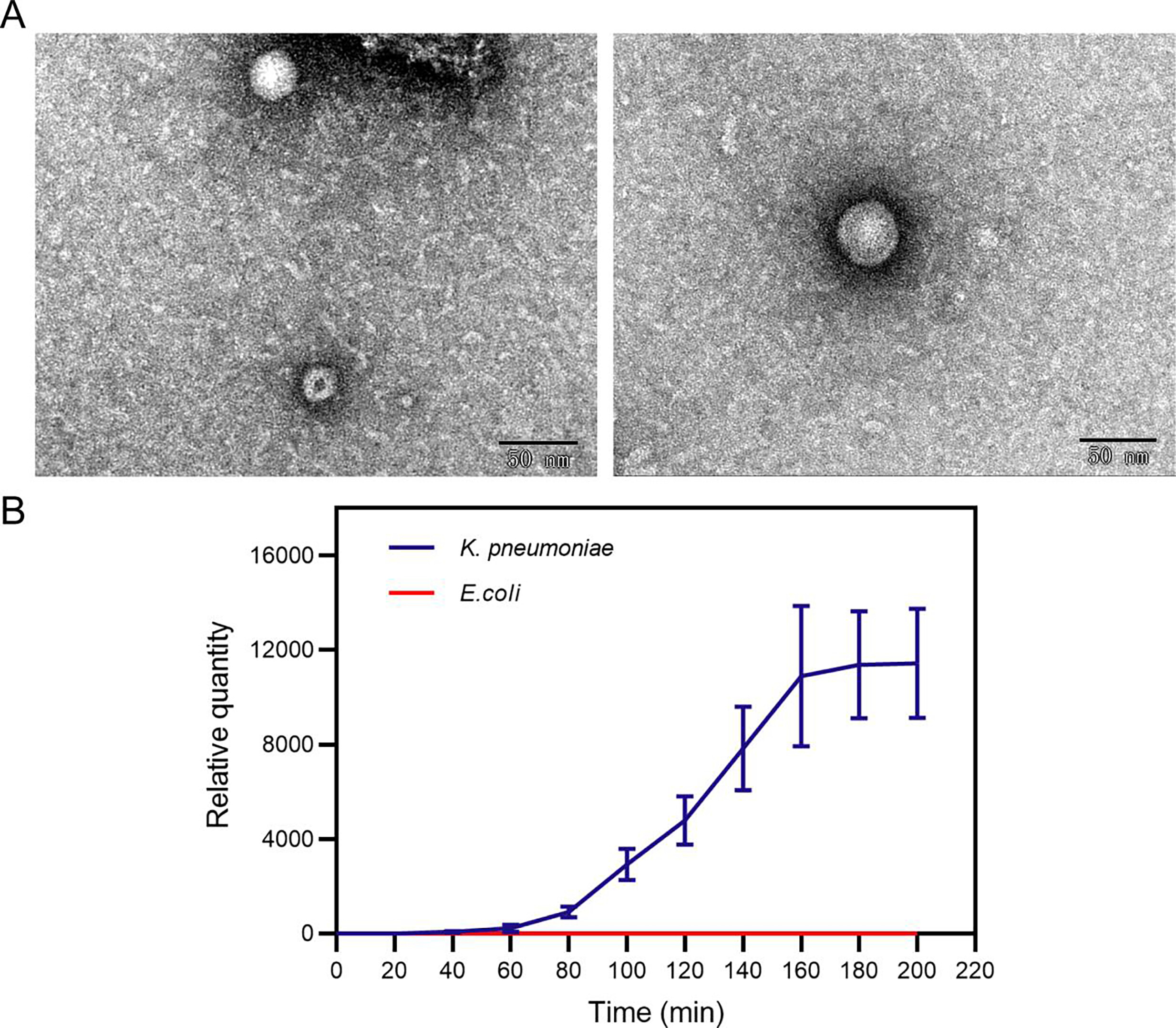
The RNA phages offer promising applications in biotechnology, including vaccine development and drug delivery. However, their potential remains underexplored due to the limited number of known RNA phages, partly because conventional methods fail to identify plaque-invisible lytic phages that do not form plaques. Here, we introduced a novel method that combines RNA-inclusive metagenomic studies and quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (RMS-RT-qPCR) to identify and characterize active RNA phages from environmental samples. This study led to the discovery of a new active Qbeta-like phage, named Cute. Genomic analysis revealed that Cute is a new member of the Qubevirus genus. Although Cute does not form plaques, it can be observed to continuously release into the supernatant when co-cultured with the host by RT-qPCR detection. This discovery underscores the potential diversity of RNA phages in nature and the limitations of traditional culture-dependent techniques. Our findings suggest that RMS-RT-qPCR could aid in the discovery of active RNA phages with significant biotechnological applications.
Read here: https://journals.asm.org/doi/full/10.1128/jvi.01637-24