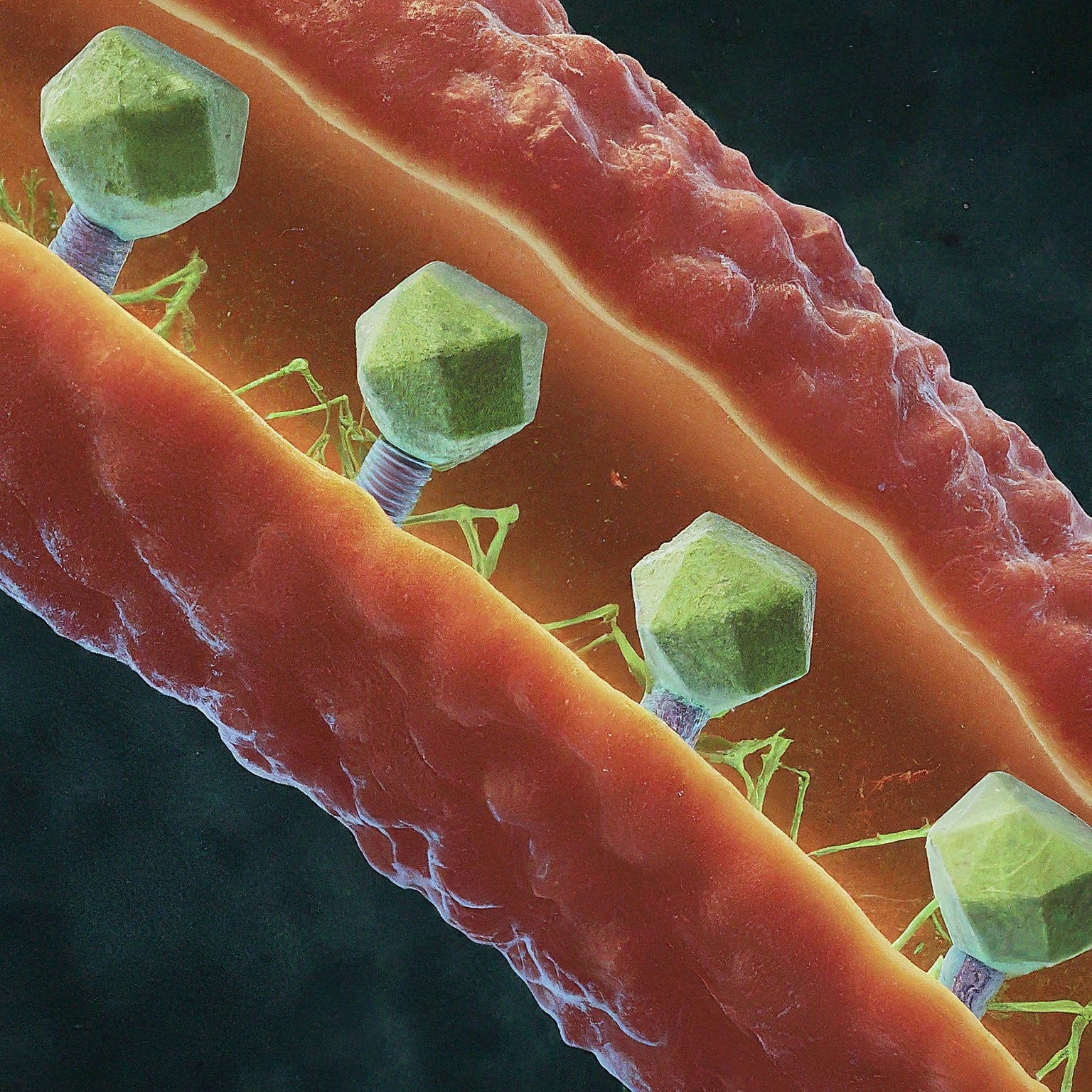
- Bacteria conjugate ubiquitin-like proteins to interfere with phage assembly
Several immune pathways in humans conjugate ubiquitin-like proteins to virus and host molecules as a means of antiviral defence. Here we studied an antiphage defence system in bacteria, comprising a ubiquitin-like protein, ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes E1 and E2, and a deubiquitinase. We show that during phage infection, this system specifically conjugates the ubiquitin-like protein to the phage central tail fibre, a protein at the tip of the tail that is essential for tail assembly as well as for recognition of the target host receptor. Following infection, cells encoding this defence system release a mixture of partially assembled, tailless phage particles and fully assembled phages in which the central tail fibre is obstructed by the covalently attached ubiquitin-like protein. These phages show severely impaired infectivity, explaining how the defence system protects the bacterial population from the spread of phage infection. Our findings demonstrate that conjugation of ubiquitin-like proteins is an antiviral strategy conserved across the tree of life.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07616-5
2. The ubiquitin-like protein UBTD1 promotes colorectal cancer progression by stabilizing c-Myc to upregulate glycolysis
Dysfunction of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) is involved in the pathogenesis of various malignancies including colorectal cancer (CRC). Ubiquitin domain containing 1 (UBTD1), a ubiquitin-like protein, regulates UPS-mediated protein degradation and tumor progression in some cancer types. However, the biological function and mechanism of UBTD1 are far from being well elucidated, and its role in CRC has not been explored yet. In our study, we analyzed CRC patients’ clinical information and UBTD1 expression data, and found that the expression of UBTD1 in cancer tissue was significantly higher than that in adjacent normal tissue. Higher UBTD1 expression was significantly associated with poorer survival and more lymph node metastasis. Overexpression of UBTD1 could facilitate, while knockdown could inhibit CRC cell proliferation and migration, respectively. RNA-seq and proteomics indicated that c-Myc is an important downstream target of UBTD1. Metabolomics showed the products of the glycolysis pathway were significantly increased in UBTD1 overexpression cells. In vitro, we verified UBTD1 upregulating c-Myc protein and promoting CRC cell proliferation and migration via regulating c-Myc. UBTD1 promoted CRC cells’ glycolysis, evidenced by the increased lactate production and glucose uptake following UBTD1 overexpression. Mechanistically, UBTD1 prolonged the half-life of the c-Myc protein by binding to E3 ligase β-transducin repeat-containing protein (β-TrCP), thereby upregulated the expression of glycolysis rate-limiting enzyme hexokinase II (HK2), and enhanced glycolysis and promoted CRC progression. In conclusion, our study revealed that UBTD1 promotes CRC progression by upregulating glycolysis via the β-TrCP/c-Myc/HK2 pathway, suggesting its potential as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in CRC.